AFNS Tenses preparation for the initial test is compulsory. The Tenses in the AFNS exam are in the form of a verb that expresses the time of an action or event. It indicates whether something happened in the past, is happening in the present, or will happen in the future. For example, in the sentence “She studies regularly,” the verb “studies” shows a present tense, while “She studied yesterday” shows the past tense. Tenses are essential in forming correct sentences and understanding English grammar effectively.
AFNS Verbal Test
Tense Preparation for the AFNS Exam PDF Free Download
Types of Tenses Come in the AFNS Initial Test
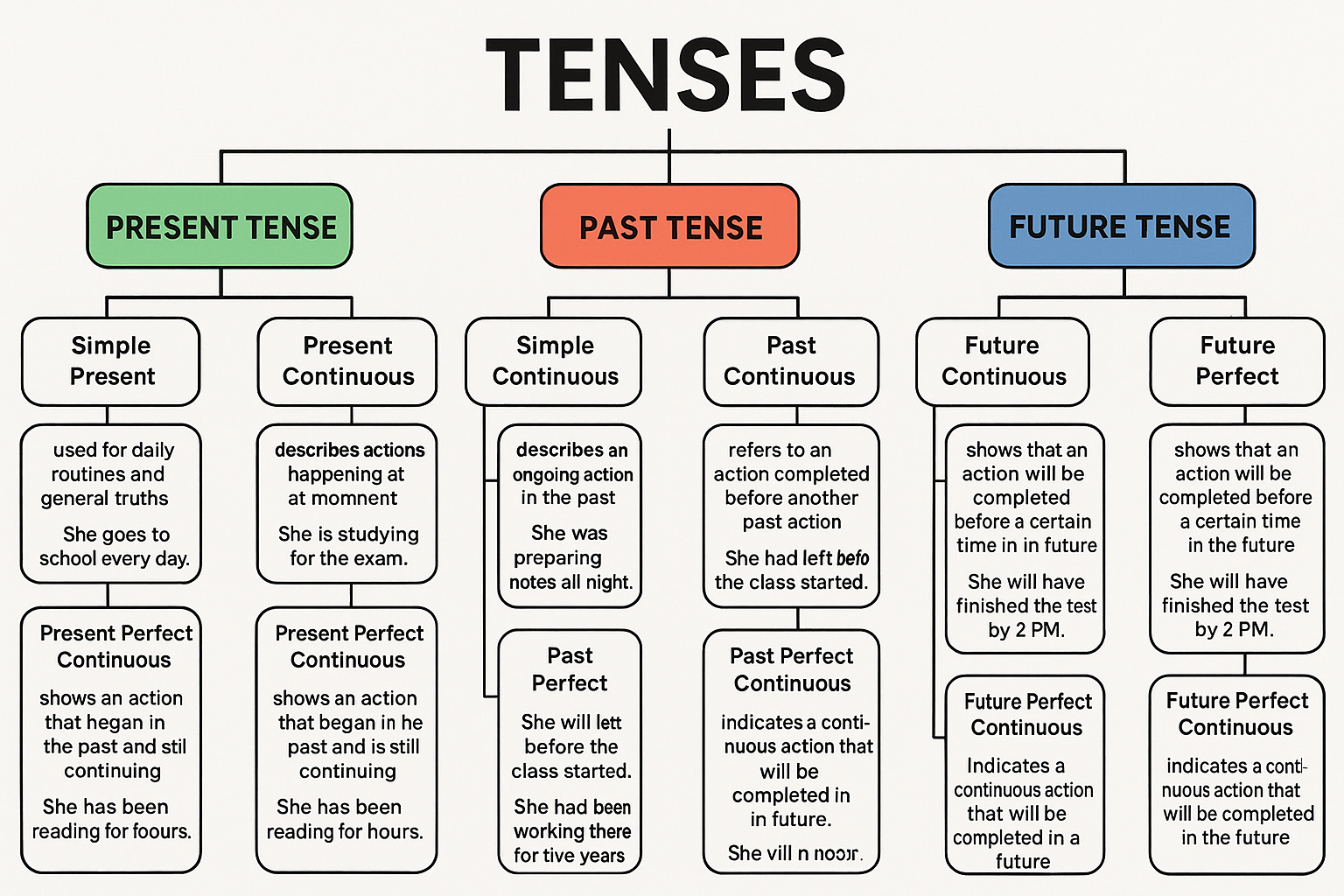
There are three main types of tenses in English grammar, and they come in the AFNS in the initial test: preparation. These tenses include the Present, Past, and Future. Each is further divided into four subtypes: Simple, Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous.
Present Tense
The present tense is used to describe actions that are currently happening or habitual actions. For example, “She drinks milk every morning” expresses a daily routine.
- Simple Present: It is used for daily routines and general truths.
Example: She goes to school every day.
This sentence shows a habitual action. - Present Continuous: It describes actions happening at the moment.
Example: She is studying for the exam.
This sentence refers to an action occurring now. - Present Perfect: It refers to actions that happened at an unspecified time before now.
Example: She has completed her assignment.
This indicates the work was done recently, without mentioning the exact time. - Present Perfect Continuous: It shows an action that began in the past and is still continuing.
Example: She has been reading for two hours.
This implies that the action started earlier and is ongoing.
Past Tense
The past tense is used to describe actions that have already happened. For example, “She prepared for the interview yesterday” shows a completed action.
- Simple Past: Used for a completed action in the past.
Example: She visited the hospital yesterday. - Past Continuous: Describes an ongoing action in the past.
Example: She was preparing notes all night.
This shows a continuous action that was happening over a duration. - Past Perfect: Refers to an action completed before another past action.
Example: She had left before the class started.
This indicates which event occurred first in the past. - Past Perfect Continuous: Shows a past action that continued for a while.
Example: She had been working there for five years.
It tells us how long she had been doing the activity before something else happened.
Future Tense
The future tense is used to describe actions that will happen. For example, “She will join the nursing academy next month” describes an upcoming event.
- Simple Future: Used for actions that will happen in the future.
Example: She will appear in the AFNS exam. - Future Continuous: Describes actions that will be ongoing at a future time.
Example: She will be attending the training session.
It emphasizes that the action will be in progress at a specific time. - Future Perfect: Shows that an action will be completed before a certain time in the future.
Example: She will have finished the test by 2 PM. - Future Perfect Continuous: Indicates a continuous action that will be completed in the future.
Example: She will have been studying for three hours by noon.
This shows the duration of an action that will continue until a specific point in the future.
Importance of Tenses in AFNS Preparation
Understanding and using tenses correctly is crucial for clearing the English portion of the AFNS exam. Many grammar-based MCQs are centered around tense identification and sentence correction. For instance, candidates may be asked to choose between “She goes” or “She went” based on the context of the sentence. A strong grasp of tenses helps avoid common grammatical errors, especially in fill-in-the-blank and spotting-error questions. Additionally, tenses appear in paragraph comprehension, error detection, and even sentence arrangement questions.
Conclusion
Tenses form the foundation of English grammar. For AFNS aspirants, mastering all 12 forms of tenses with correct usage and examples is essential. Understanding when to use “has,” “had,” or “will have” can make a significant difference in accuracy. Daily practice, sentence construction, and revision of rules will improve both confidence and command over grammar.